CBD vs. THC: What's the Difference?
As more nations jump onto the legalization bandwagon, the popularity of cannabis continues its meteoric rise. In parallel, awareness of CBD products continues to gain traction.
So what's the difference between CBD and THC in our beloved cannabis plants? This article will examine both compounds' applications, similarities, differences, and what you need to know to decide what suits you.
What is CBD?
CBD is cannabidiol, a natural compound and one of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. CBD has gained traction rapidly due to its potential health benefits [1] and non-psychoactive properties that will not get you "high."
The compound is extracted from hemp plants, which according to the 2018 Farm Bill, cannot contain more than 0.3% tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is the compound responsible for the high that cannabis causes.
Hemp products are legal in many parts of the world, while psychoactive cannabis products are not. CBD is commonly made into edibles, oils, tinctures, and topical applications.

What is THC?
THC stands for tetrahydrocannabinol, a natural compound found in the cannabis plant and one of the many cannabinoids present in cannabis. THC is primarily known for its psychoactive properties and is responsible for the side effects and "high" commonly associated with cannabis use.
There are multiple types of THC, but delta-9 is the most common and sought-after for its psychoactive effects. These include euphoria, relaxation, altered perception of time, increased appetite, and potential memory impairment.
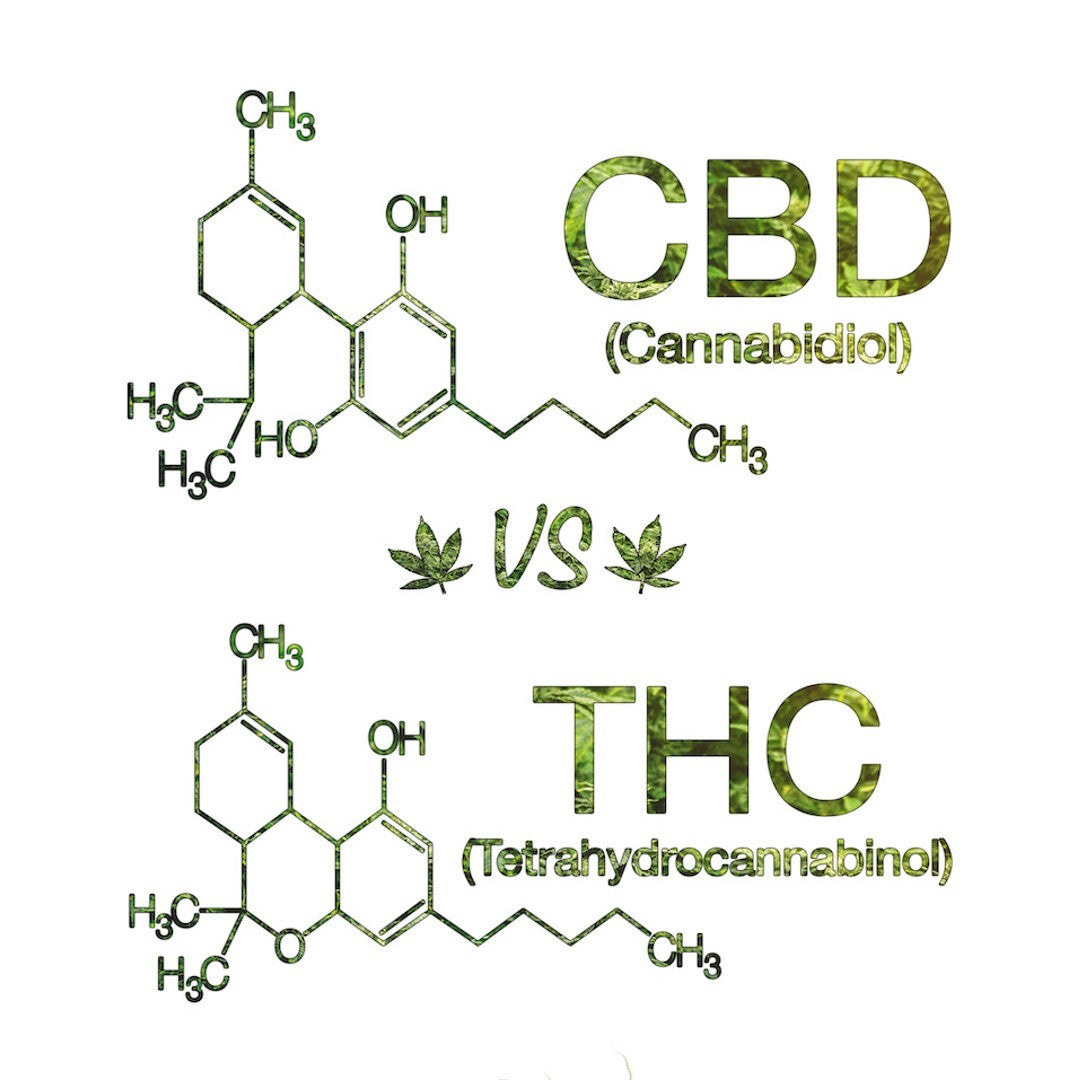
CBD vs. THC: Chemical Composition
Chemical structure: CBD and THC have the same molecular formula - 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms (C21H30O2). However, their atoms are arranged differently, leading to two distinct compounds with different effects.
Similarities
Both CBD and THC interact with the body's endocannabinoid system, which consists of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids. The endocannabinoid system influences and regulates various physiological processes, including pain perception, mood, immune response, and more.
Differences
One of the key differences is that THC is psychoactive and can produce a euphoric "high" when used. In contrast, CBD is non-intoxicating and does not induce this effect.

CBD vs. THC: Effects on the Body
CBD does not directly bind to the endocannabinoid system's receptors as THC does. Instead, it activates other receptors like serotonin [2].
THC binds to the cannabinoid receptors, activates them, and produces psychoactive effects.
THC and CBD combined may result in an "entourage effect," which magnifies the effects of the compounds due to the mixture of terpenes and cannabinoids*.
CBD vs. THC: Legal Status
CBD is legal in many parts of the world, including the US, Canada, and the UK. CBD products like oils and edibles can be widely found online, in head shops, and in grocery stores. CBD products must contain less than 0.3% THC (US) and 0.2% (UK) to be legal by federal law.
On the other hand, THC products continue to be classed as controlled substances and are illegal in many parts of the world. While medical cannabis is fast gaining traction, recreational use of cannabis products is still banned in many countries.
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Sources
[1] Cannabidiol use and effectiveness: real-world evidence from a Canadian medical cannabis clinic
Rapin et al.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8223341/
[2] Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain
De Gregorio et al.