The medicinal use of Cannabis has been prevalent for centuries. Many civilizations have used cannabis in their own ways and have touted its effectiveness with a host of issues relating to the human body. The Cannabis genus, which can further be broken down into the plant species of hemp and marijuana, showcases its effects when it comes in contact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system, or ECS.
This biological system was discovered by scientists in the early 1990s who realized that the ECS balances various functions of the body. The hemp and marijuana plants provide us with cannabinoids that interact with our ECS and revitalize our body functions. Thus, the cannabinoids extracted from the Cannabis plants help balance the ECS thereby improving the functions that it supports.
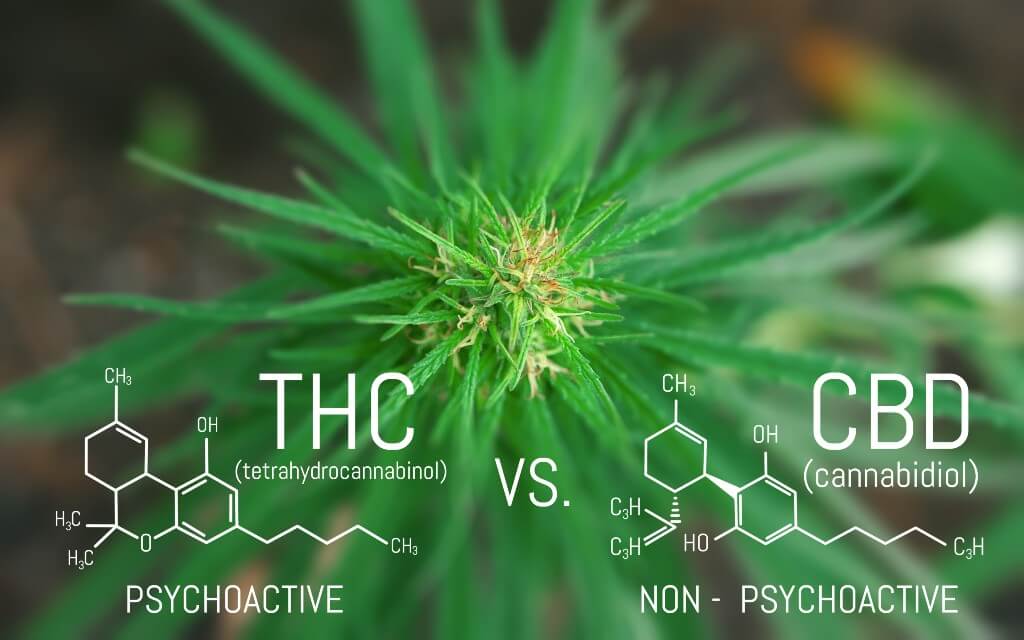
What is THC?
We need to understand that there are over 100 cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant, but Cannabidiol (CBD) and Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the most renowned and widely recognized cannabinoids in the world. Both CBD and THC can be extracted from hemp and marijuana plants respectively but while CBD is a non-psychoactive compound, THC, when taken in large quantities, can invoke a sense of euphoric high, unlike its counterpart, CBD.
Even though THC is present in both hemp and marijuana plants, the levels of THC in hemp are far lower as compared to a marijuana plant. So when CBD is extracted from a hemp plant, it naturally contains way less than a 0.3% level of THC as prescribed by the 2018 Farm Bill. Hence, CBD products will not give you the sense of high that THC products might provide, unless you are purposely adding up to that 0.3% of THC.

What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is present in every mammal. The ECS comprises receptors that are present in most areas of the body. The primary function of the ECS is to achieve homeostasis, a biological state in which each body function is working at its optimum capacity, providing an effective balance to the entire human anatomy.
To put it mildly, the ECS is a system present in the human body that interacts with cannabinoids and endocannabinoids to support functional balance. The receptors present in the ECS bind with the cannabinoids from the hemp and marijuana plants which help to regulate the digestive system, vascular system, reproductive system, musculoskeletal system, nervous system and immune system.
The two main receptors of the ECS are CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are found in the brain and the central nervous system which affects your appetite, motor activity, immunity, short term memory and thinking while CB2 receptors are present in the peripheral nervous system which regulates involuntary body functions like breathing and heartbeat.
How Does THC Affect the Endocannabinoid System?
THC binds with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS. The cannabinoid receptors in the body have important bodily functions to accomplish and sometimes due to some deficiency in your body’s natural cannabinoids, fail to do their job. Hence, the cannabinoids from hemp and marijuana act as a regenerating fuel or spark that helps the cannabinoid receptors in the ECS to accomplish their goals. The cannabinoids from the hemp and marijuana plants help to stimulate the human body’s endocannabinoid receptors and work hand-in-hand with the ECS.
THC also has a psychoactive effect that gives you a feeling of euphoria. The most interesting fact about THC’s chemical structure is its similarity with another chemical in the brain named Anandamide, which functions as a neurotransmitter. Anandamide sends chemical messages between different nerve cells in the central nervous system. This directly affects sensory experiences such as pleasure, memory, concentration, coordination, movement and perception of time.
Because of similarities in the chemical structures between THC and Anandamide, the body treats the THC molecules as Anandamide and allows them to bind with the endocannabinoid receptors easily.
How Long Does it Take for THC to Work?
THC usually works quickly, but it mostly depends on the way you ingest it. You can use THC oil products and put them under your tongue. This will usually take around 15-30 minutes before you feel its effects. The effects may vary from person to person and also on the quantity of your dosage, but many will feel the effects of THC within the first half hour.
Smoking or vaping will allow the effects of THC to settle in quicker, within 10-15 minutes or even faster, but the euphoria will wear off after 1-2 hours. While smoking or vaping may be a common mode of ingesting THC, gummies, oils, tinctures, sprays and salves are also different modes of ingestion available to the users.
You need to remember that if you frequently use THC, it will remain for a longer period in your body and also in higher quantities. For people who take THC once a day or more, tests may show THC concentration levels in their system for 30 days or longer. This window becomes smaller if you bring the intake level of THC down.
Does THC Show Up in Blood and Urine?
It is incredibly difficult for the human body to quickly metabolize THC and flush it out of the system. If you are planning to drink heaps of water to remove the THC out of your system so you can pass your test, think again. Urine tests can detect levels of THC for approximately 3 to 30 days after its use. But the case is different for blood tests.
With blood, THC usually disappears after 12-24 hours of its usage. But you should know that since the body metabolizes THC slowly, the blood test may still turn up positive. Regardless of how you take THC into your system, it will appear in blood, urine, or saliva tests.

How Does THC Affect Your Workout Regimen?
THC may lead to irregularities in the heartbeat for some. It is always better to have an exercise plan that doesn’t coincide with your intake of THC. Since THC is prone to give you a sense of euphoric high, the body before the workout might feel different than usual and your judgment could potentially become impaired when it comes to lifting weights.
Even though many athletes have acknowledged the use of THC in their lives, its effects on their performances are still a gray area. The idea that THC boosts performance or strength is still waiting to be explored.
Final Thoughts
By now, you have a fair share of ideas about the effects of THC and how it works in your body. You have most of the ingredients to make an informed decision about which THC product will work best for you. THC’s relation with the endocannabinoid system is now known and being studied more and more. This information should help you to create a CBD or THC-based regimen that tends to your needs and supports your lifestyle. It’s best to start slow and experience lower levels of THC. After trying it out and understanding its effects, you’ll know better how to dial in your personal dosage.